Excessive bodyweight contributes to a host of illnesses. Diets and lifestyle changes, physical activity and exercise programs can contribute to successful weight loss, but for a group of patients morbid obesity remains a significant problem. Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery has been on the increase.
Opinions about the usefulness of bariatric surgery have been divided. Often it was seen as a heroic effort with lots of risks and questionable benefits. In some procedures patients did not show significant weight loss, and there were some doubts whether the risk of surgery was worth taking.
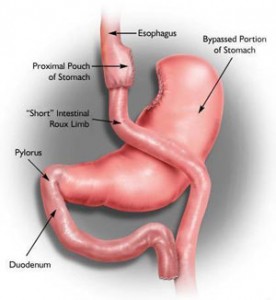
Dr. Lars Sjoestroem of Gothenburg University has a detailed study on 4,047 Swedish patients with obesity, of which 2,010 underwent bariatric surgery, while 2,037 received non-surgical treatment. The two groups were compared for overall mortality after 11 years. The non-surgical control group lost little or no weight. The bariatric surgery patients did better. The most successful group was the one which received gastric bypass surgery with a weight loss of 25%. Vertical-based gastroplasty patients lost 16% of their weight, and those who underwent gastric banding lost 14% of their weight over 10 years.
At follow up the overall mortality was significantly decreased in the group that underwent surgery. Death risk from disease which is associated with obesity, such as coronary artery disease was significantly decreased by 56%. The risk of death from diabetes was decreased by 92% and the risk of death from cancer also showed a reduction of 60%.
US data show similar results of a decrease in long-term mortality in obese patients who underwent bariatric surgery and lost weight.
More information on weight loss: http://nethealthbook.com/womens-health-gynecology-and-obstetrics/weight-loss/
Reference: August 23, 2007 issue of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Last edited November 3, 2014