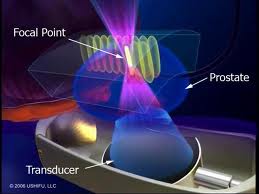
High-intensity focused ultrasound, also known as HIFU is a treatment that prostate cancer patients are seeking out. The treatment technique is minimally invasive, has low risks of impotence and urinary incontinence and can be done on an outpatient basis. It is a two to three hour procedure which can be done with some mild sedation and spinal anaesthesia, and generally men can resume their normal lives immediately after surgery with the knowledge of being cancer-free. Dr.Ian Brown, the medical president of the Niagara HIFU clinic in Niagara Falls, Ontario likens the technique to the effect of a magnifying glass that focuses sunrays on a leaf and burns it. Except there is no sunlight, but a pulse of high-energy ultrasonic waves focused onto a specific area of the prostate. Temperatures reach approximately 90 °C (= 194 °F), until the cancer cells are dead. The transducer is equipped with ultrasonic imaging, so the treating physician can see the entire prostate gland on a monitor, and as a result surrounding nerve structures that are responsible for erectile function are not damaged. There is some inconvenience for the patient after the surgery. He has to wear a catheter for two to three weeks until he can urinate on his own. Like any prostate cancer treatment, HIFU also has potential side effects like retrograde ejaculation or urethral fistula.
Reports state that these side effects are minimalized with HIFU, but they are not eliminated. This treatment is not suitable for every patient. Patients with early stage prostate cancers are suitable candidates. HIFU is not available in the US at present, but has been approved by Health Canada in 2004 based on European data. It is not covered by health insurance, and at $20,000 this new costly option is not affordable for everybody.
More information about prostate cancer: http://nethealthbook.com/cancer-overview/prostate-cancer/
Reference: National Review of Medicine, March 2008, page 35, 39
Comment: Here is an update regarding FDA approval in the US. According to the FDA panel there is not enough solid data to confirm effectiveness or safety, so it was not approved in 2014.
Last edited November 3, 2014