Weight loss is easier for some than others, because metabolism can vary in people. In the following I will outline this in more detail. A biochemist recently published an article in “the conversation”, which is the basis for my review.
Everybody has their own metabolism
It is important to realize that everything that our body comes in contact with influences our physical characteristics like our blood pressure and our energy. Together all the biological characteristics have the name phenotype. The most important factor that influences our phenotype is our metabolism. It matters what you do like eating, whether you are taking medication, smoking, or exercising. This all influences your metabolism. On a molecular level it starts when your digestive system breaks nutrients down into each component: carbohydrates, fats and protein. When your digestive juices break down these food components, electrons are released from chemical bonds. These are transferred to the mitochondria, the energy packages in all of our cells. It is important to note that we do not all have the same metabolism as our neighbour. There are different types of metabolism.
Metabolism of an elite athlete
Elite athletes are not born that way. They have to practice hard physically for many hours a day and do that over several years. Their bodies adapt to the regular training by creating extra mitochondria in every cell of their body. Their body also learns how to burn fat, carbs and amino acids into chemical energy effectively. The elite athlete has superior energy production.
Metabolism of a Covid-19 patient
At the other end of the spectrum is the metabolism of a Covid-19 patient. Researchers found by examining patients who got sick from Covid-19 that their fat metabolism was impaired. This inability to burn fat persists in long Covid patients. The fatigue from long Covid is due to a dysfunction of the mitochondria. The mitochondria are not producing enough energy.
The in-between metabolism of blood donors
Travis Nemkov is an assistant research professor at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus. His team investigated blood from 13,000 blood donors. They found that the metabolism of blood donors placed between the metabolism of elite athletes and that of Covid-19 patients. They also found a lot of variation of a metabolite by the name of kynurenine, which is due to a breakdown of the amino acid tryptophan. The researchers found that blood from donors with higher kynurenine levels was unable to restore blood levels of blood recipients. In addition, they found that kynurenine levels were higher in older donors and also in patients with obesity (higher BMI’s). Kynurenine was also a strong predictor for Covid-19 severity.
Weight loss problems when the metabolism is slow
We all know people who have a problem shedding their weight compared to others who loose weight with only a few days of food restriction. “People might have fast, slow, or average metabolism, regardless of their body size and composition,” says Dr. Chih-Hao Lee, professor of genetics and complex diseases at Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health. This Harvard University website explains this in detail. How do we speed up a naturally slow metabolism? We can exercise a bit more, and watch the quality of our food intake. This means cutting out added sugar, too much fat, too many carbohydrates and processed foods. The Harvard website says: “Studies have found green tea contains a compound called epigallocatechin gallate, which may increase the calories and fat you burn. “By making these small changes mentioned you can rev up your metabolism.
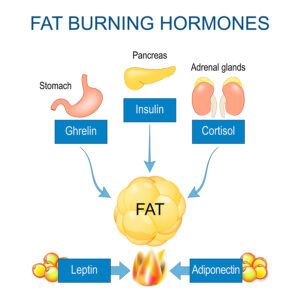
Hormones and body weight
Our metabolism and body weight depend on a number of hormones: leptin, insulin, estrogens, androgens and growth hormone play a crucial role in weight control. Additional hormones, such as the thyroid hormones are involved in maintaining our weight in a healthy range. Researchers have noticed that patients with hypothyroidism gain weight and burn less calories in their mitochondria. On the other hand, patients with hyperthyroidism stimulate their metabolism, lose weight and burn more calories. The exact mechanism of how thyroid hormones interact with the other hormones is unknown.
Conclusion
I came across a review about metabolism and weight control, written by a biochemist. He pointed out that different people have different metabolisms. Examples he gave were the metabolism of elite athletes and the metabolism of Covid-19 patients, who are at the low end. His team investigated the metabolism of 13,000 people who were blood donors. He called them people with an in-between metabolism.
How to speed up naturally slow metabolism
How do we speed up a naturally slow metabolism? We can exercise a bit more, and watch the quality of our food intake. This means cutting out added sugar, too much fat, too many carbohydrates and processed foods. Your physician can also tell you whether your thyroid hormones and your human growth hormone are adequate. Other hormones that regulate your metabolism are leptin, insulin, estrogens and androgens. When you look at the factors that are responsible for your metabolism, the genetic factors come first. Your hormone status, eating pattern and exercise status come second. But by making small changes to the factors mentioned you can rev up your metabolism significantly.