Notably, conventional medicine has nothing to offer against advanced cancer, but stimulating the immune system leads to better cancer survival.
Dr. Hoffer’s survival experiment with incurable cancer patients
The following is a description of a 9-year follow-up of incurable cancer patients. They were given supplements known to stimulate the immune system and their survival rates were recorded. Ref. 1 describes the experiment by Dr. Hoffer, the father of orthomolecular medicine. It is important to realize that this is a branch of medicine that uses large doses of vitamins and minerals. This can rectify metabolic changes in various diseases. Dr. Hoffer treated 131 advanced cancer patients between 1976 and 1988 with a mixture of mega vitamins and minerals. There was a control group (not taking any supplements) and the experimental group.
Results regarding incurable cancer patients over 9 years
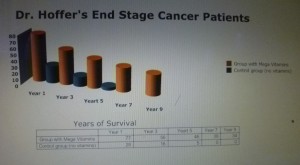
In fact, the results of this 9-year follow up study are depicted in the image below. The Y-axis represents the % of survival (at the zero point of time 100 % of each group were alive), the X-axis shows the time of survival in years. To clarify, the group of cancer patients taking meta vitamins is depicted with orange columns, the control group with blue columns. At 7 years of follow-up none of the controls survived. Explicitly, there was an 8-year survival advantage of the mega vitamin group versus the control group (control group 28% survival at year 1 of follow-up, mega vitamin group 34% survival at year 9 of follow-up).
List of supplements patients in the experimental group took daily
With this in mind, here is the detailed list of the supplements that Dr. Hoffer instructed his experimental group cancer patients to take daily.
Vitamin C, 10,000 to 40,000 mg orally daily; B3 vitamin (niacin or niacinamide) 300 to 3,000 mg; vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) 200 to 300 mg; folic acid 1 to 30 mg; vitamin E succinate 400 to 1,200 IU; Coenzyme Q10 300 to 600 mg; selenium 200 to 1,000 micrograms daily; zinc 25 to 100 mg; calcium and magnesium supplement (2:1 ratio); mixed carotenoids as carrot juice; multivitamins and minerals.
Ref. 1 (page 347) explains that in this case the Mayo Clinic did a study where they “duplicated” Dr. Hoffer’s study by using only high doses of vitamin C. It is important to realize that they failed to show any cancer fighting effect. However, they neglected to include all of the other cancer fighting supplements listed above. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that stimulates the immune system partially, but does not fight cancer by itself.
Strengthen your immune system by taking 14 supplements
In the following I like to share what I found when I investigated what supplements are necessary for optimal immune responses. The Linus Pauling Institute wrote a detailed review of the literature on the topic regarding “Immunity in depth”. It is published by the Oregon State University.
Essentially, there were 14 supplements that are listed below that were critical for the immune system to fully respond.
In the following I listed the 14 supplements, but, if they were present in Dr. Hoffer’s clinical cancer trial, I inserted them right after each item. 8 out of 14 supplements overlapped between Dr. Hoffer’s supplements and the supplements necessary to stimulate the immune system. There is a total overlap of 57%.
- Vitamin A: mixed carotenoids as carrot juice
- Vitamin B6: vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) 200 to 300 mg
- B12 vitamin
- Folic acid: folic acid 1 to 30 mg
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C, 10,000 to 40,000 mg
- D3 vitamin: Ray Schilling’s answer to Can vitamin D lower your risk of CoVID-19?
- E vitamin: vitamin E succinate 400 to 1,200 IU
- Iron
- Copper
- Selenium: selenium 200 to 1,000 micrograms daily
- Magnesium: calcium and magnesium supplement (2:1 ratio)
- Zinc: zinc 25 to 100 mg
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Probiotics
Dr. Hoffer’s additional vitamins and minerals were: multivitamins and minerals; Coenzyme Q10 300 to 600 mg; and vitamin B3 (niacin or niacinamide) 300 to 3,000 mg. The 5 items that were missing in Dr. Hoffer’s clinical trial were vitamin B12, vitamin D3, iron, copper and probiotics.
Discussion
During the Covid epidemic the importance of the immune system for survival became very clear. One of the current mysteries regarding the immune system is why some people develop only very mild symptoms with Covid, while others get deadly sick. The other question has been around much longer: when it comes to cancer survival, why are there long-term survivors with some advanced cancers, but others perish. I believe that the key is how well the immune system is functioning. Dr. Hoffer’s end stage cancer survival trial achieved a 34% survival of cancer patients at year 9 of the clinical trial. At that time 100% of the control group were dead. Indeed, this is a remarkable finding.
Supplementation with vitamins and minerals prolonged cancer survival
The only difference was the supplementation with 57% of the Oregon University list of supplements necessary to stimulate the immune system. One of the more important supplements, namely vitamin D3 was not even included and yet there was a 34% survival in the experimental group after 9 years. Conventional medicine concentrates on surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy as the major therapeutic tools to fight cancer, but there is rarely if at all the mention of supplements. Ordinarily end stage cancer patients live on average 3 to 6 months.
Mayo Clinic’s attempt to jeopardize Dr. Hoffer’s cancer survival findings
When the Mayo Clinic got wind of Dr. Hoffer’s clinical trial they quickly attempted to “duplicate” the findings, but they left everything out except mega doses of vitamin C. Then they proclaimed that Dr. Hoffer’s data were flawed. In reality they failed to duplicate the findings, because they were poor copycats. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, but it won’t be of help to cancer patients on its own. As the Oregon State University publication showed, there are 14 supplement that are necessary to work in symbiosis to stimulate to immune system to fight cancer.
It is significant that there was a 57% congruence between Dr. Hoffer’s list and the Oregon State University list of supplements to stimulate the immune system. Future cancer clinicians should revisit Dr. Hoffer’s clinical findings and finetune them to increase the long-term cancer survival times. For one, the supplement list should include vitamin D3, probiotics and omega-3 fatty acids.
Stimulating the Immune System Leads to Better Cancer Survival. (Image source).
Conclusion
Dr. Hoffer did a clinical trial that lasted 9 years between 1976 and 1988. Some patients were recruited earlier than others, but all were observed for a total of 9 years. He treated end-stage cancer patients with vitamin and mineral supplements. A control group that did not take any supplements was included in the trial. After 9 years the experimental mega vitamin group had a survival of 34%. None of the controls that did not take any supplements were still alive after 7 years. The literature by the Oregon University showed that 14 supplements are necessary to support the immune system. Dr. Hoffer’s clinical trial used 57% of these supplements. I am postulating that the good results of the mega vitamin group with respect to cancer survival likely comes from a strengthening of the immune system with the supplements.
The future of cancer treatments
Cancer treatments are entering a new phase where with the help of multiple treatment modalities combined (photodynamic therapy or PDT, immunostimulation, oxygen therapy and low-dose laser activated chemotherapy) it is now possible to cure many cancers that were untreatable in the past. The tunnel vision approach of conventional oncology with only a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy is obsolete for cases where cancer has metastasized. At this point the methods described here are promising, but have to be still considered experimental until larger clinical trials confirm Dr. Hoffer’s findings.
Reference
Ref. 1: Andrew W. Saul, PhD: “The Orthomolecular Treatment of Chronic disease”, Basic Health Publications Inc., Laguna Beach, CA 92651, 2014.
Dr. Hoffer’s cancer survivor experiment (part of the above) was previously published here.





