Drug resistant bacteria (like MRSA, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus) have developed in many hospitals and have caused more than 2 million infections in the US alone of which 90,000 people died. Yet so far research regarding this problem has been very slow and unsuccessful. In Canada there was an outbreak of E.coli, which left 14 people severely ill and simultaneously there was a similar outbreak in the US leaving three people dead.
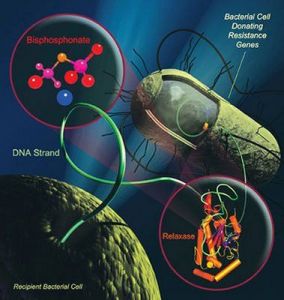
Dr. Redinbo, PhD in biochemistry and biophysics, from the University of North Carolinaat Chapel Hill made an astounding discovery in his lab. He tested some of the older medications used for osteoporosis treatment, the biphosphonates clodronate and etidronate, to see whether they would have an effect on stopping the multiplication of these harmful bacteria. Dr. Redinbo’s work was published in the July 13 edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Dr. Redinbo’s team found that an enzyme, called relaxase, is at the center of the development of antibiotic resistance. When resistance develops, there is a genetic transformation that takes place, like a mini Darwinian selection process where the most resistant bacteria survive and multiply. The resistant bacteria mate with each other and with bacteria that are not yet resistant. This process involves the relaxase enzyme system, some DNA stranding and a strand exchange. In this way new resistant bacteria are formed. Experiments under the supervision of Dr. Redinbo found that this process can be stopped by the phosphate-rich compound, biphosphonates (clodronate and etidronate). Other chemicals were found to not be as effective.
The relaxase system is found in a number of problem bacterial strains, Staphylococcus strains, drug resistant Acinetobacter strains and others. Unfortunately the biphosphonates have some side-effects like stomach soreness and birth defects. The researcher said that he hopes that these drugs and perhaps others with less side-effect will offer new treatments for antibiotic resistant bacteria.
Reference: July 13, 2007 edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Last edited December 5, 2012