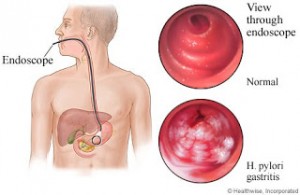
Indigestion, heart burn, bloating and stomach discomfort are common problems. Often the reason is simple. Too much food and drink at a party, a plateful of deep fried Buffalo wings or a midnight order of double-pepperoni pizza will contribute to stomach upset and a bad night’s sleep. A few over the counter antacids will come to the rescue. If indigestion is a faithful but miserable daily companion, the excuse of “just having a sensitive stomach” becomes a form of denial and a dangerous form of self diagnosis. Something is wrong, and it is time to seek medical attention instead of over the counter meds. The first line of defense will be prescription drugs called “proton pump inhibitors” (PPI). They are designed to eradicate excessive acid production in the stomach. If symptoms are more severe, e.g. weight loss, a gastroscopy will be necessary. Even though the prevalence of a stomach infection with Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori) is declining, about 30% of patients with chronic stomach upsets test positive for an infection with these bacteria. This can cause recurrent stomach pains. In this case it becomes necessary to treat this with a combination of PPI’s and antibiotic medication. Eradication of H.pylori can mean a cure from a stomach ulcer. It also reduces the risk of developing gastric adenocarcinoma, a form of stomach cancer that could have developed out of an untreated gastric ulcer. Just because a person has heartburn does not mean that the condition is due to gastro-esophageal reflux of stomach acid. If after treatment with a PPI the problems of indigestion, heartburn, bloating or stomach aches reoccur, lab tests can give more information. According to a prospective trial conducted by Dr. Delaney and others the H.pylori serology (a blood test) is unreliable, but other H.pylori tests like urea breath test or stool antigen are reliable tests to establish whether a stomach infection with H.pylori is present or not.
If the bacterium is present, its eradication with antibiotic therapy will stop the stomach problems in a high percentage of cases with one treatment protocol. What was surprising was that after one year the treatment result of the treatment group with PPI/antibiotic combination was as successful as the control group that was treated with PPI’s alone. It was concluded that in the more severe cases with weight loss, vomiting, or overt bleeding an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy should be performed where a direct H.pylori test from samples is also done. However, in the vast majority of cases with minor symptoms can be treated safely by the general practitioner with PPI’s and follow-up examinations in subsequent visits. Treatment failures can then be referred to a gastroenterologist, if necessary.
More information about gastritis and H. pylori: http://nethealthbook.com/digestive-system-and-gastrointestinal-disorders/gastritis/
Reference: British Medical Journal 336:623-624 (March 22, 2008)
Last edited November 3, 2014