After overindulging over the holidays, new years resolutions often have diets and life style choices high on the list.
These concerns are not something new. Doctors have had concerns about heart disease, diabetes, bulging waistlines and elevated cholesterol. For over three decades there have been concerns that elevated insulin levels may be associated with heart disease, and the constellation of symptoms was called “syndrome X” and later the “insulin resistance syndrome”.
Most recently the evils that are associated with body fat have been called the “metabolic syndrome”.The problem has assumed epidemic proportions: by 2001, 30% of US adults were considered obese with a body mass index of over 30, and 50% were overweight with a body mass index over 25. The form of type 2 diabetes (the adult onset of the disease) is predicted to double in the next 20 years. Physicians are reporting that they are seeing increasing numbers of children who are obese and suffer of type 2 diabetes. The major concern with an accumulation of body fat is the area of the abdomen (think of the “apple shape” with fat around the abdomen). This visceral fat tissue is not just innocently sitting there stopping you from closing buttons and zippers. It is very metabolically active and the substances it releases are a threat to your health. These fat cells secret pro-inflammatory substances called “cytokines.”
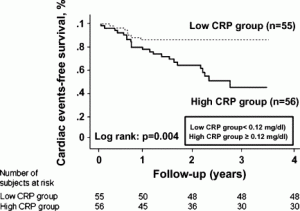
They also form substances that influence blood-clotting, factors that increase insulin resistance, substances like angiotensin, which are signing responsible for high blood pressure as well. Among the host of damaging substances is also the C-reactive protein, which is recognized as a risk factor for heart disease.
There is only one solution: to reduce the risk, excessive weight has to be shed. A sensible diet to achieve that goal has to contain less saturated fat, more fiber, and low glycemic index carbohydrates. Proper dietary habits are only one part. The other as important measure is life style intervention, which includes 2.5 to 3 hours of moderate exercise per week.
Many of the current diets promise weight loss without compromising health. All of them promote weight loss, provided they are strictly adhered to.
The high protein diets (Atkins, Protein Power Plan) are useful for rapid initial weight loss, however due to the overload of protein long term use is highly questionable. Kidney dysfunction as a consequence is a threat to health and no benefit at all!
Moderate carbohydrate diets, moderate fat, as well as moderate protein will remain the answer for long-term life style changes. It is also of significance that the glycemic index of carbohydrates plays a major role. Food intake, which favors carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, is associated with less heart disease. It has also been documented that insulin levels are more stable. Low glycemic carbohydrates include most vegetables, beans, lentils, as well as fruit like apples, pears and oranges. In contrast, high glycemic carbohydrates result in a fast insulin release, which ultimately leads to insulin resistance. Among these items are potatoes, crackers and other flour products, rice, puffed or flaked breakfast cereals, and tropical fruit (papayas, pineapple, melons).
For short-term dieters, it is an option to embark on any of the current diets without deleterious effects, no matter whether they are high-carb or low-carb. But at this point only the diets with moderate carbohydrates have shown to have some benefits on heart health.
Ultimately the wiser choice is to consume foods with a low to moderate glycemic index, by increasing the intake of vegetable proteins and oils and by choosing increased servings of vegetables and fruit instead of highly processed items. So, when you next walk through your supermarket, remember that most of the good stuff is in the periphery, namely the area where all the fresh, unprocessed or minimally processed foods are found.
More info about Mediterranean diet: http://nethealthbook.com/news/mediterranean-diet-benefits-us-workers/
Reference: Metabolic Syndrome Rounds, Oct. 2004, Vol. 2, Issues 8, St. Michael’s Hospital, University of Toronto/On/Canada
Last edited October 27, 2014