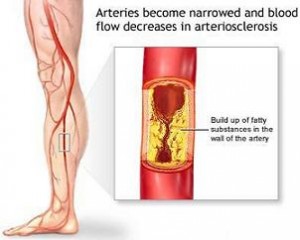
Metabolic syndrome has serious health consequences: diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease are just a few conditions that are associated with it. It is also known that diabetic patients are prone to pressure sores and ulcers of their feet and if the leg became gangrenous, the patient would lose it due to the need to amputate. Peripheral artery disease or PAD has recently been studied by Dr. Aruna D. Pradhan, and the prospective study involved 27,000 women. At the beginning of the study the middle aged women were free of cardiovascular disease, but a quarter of them had the hallmarks of metabolic syndrome. Twenty five percent of those with the condition also were diabetic. During the 13 years of follow-up 114 women developed peripheral artery disease and those patients with metabolic syndrome were 62% more likely to develop the disease. The individuals with metabolic syndrome had other features: they were less likely to exercise, more likely to smoke and their weight was higher. But 7,000 women with metabolic syndrome had another important feature in their lab tests: they had markedly higher levels of biomarkers of systemic inflammation, which was manifested in higher levels of C-reactive protein.
- Metabolic syndrome causes peripheral artery disease
Once all the criteria are stacked up against each other, it becomes obvious that the presence of metabolic syndrome alone is not responsible for the most significant increase in peripheral artery disease. It is not the high cholesterol levels or the high triglyceride readings that are the villains in this condition. The driving force is systemic inflammation, as documented by the high C-reactive protein levels in blood tests.
More information about hardening of arteries: http://nethealthbook.com/cardiovascular-disease/heart-disease/atherosclerosis-the-missing-link-between-strokes-and-heart-attacks/
American Heart Association, New Orleans, Nov. 8 to 12, 2008
Last updated Nov. 6, 2014