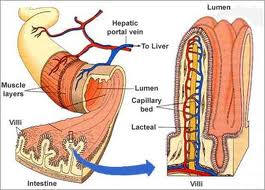
There has not been a large study in the US looking at the natural frequency of Celiac disease (CD) in the population. Celiac disease is an inborn hypersensitivity to gluten, to be more precise, a hypersensitivity to the sub-fraction of gluten, called “gliadin”, which leads to an atrophy of the villi in the small intestine.
Dr. Alessio Fasano, from the University of Maryland in Baltimore, and colleagues have examined a total of 13,145 subjects in their study to look for specific antibodies in the blood and by doing as many bowel biopsies to see how many cases of CD would be found. There were 4 groups of patients that could be identified: 4,508 first-degree relatives of CD proven patients; 1,275 second-degree relatives; 3,236 symptomatic patients who either had gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms or who had a disorder associated with CD; 4,126 patients not considered at risk and who could serve as a control group. Below are the results of the study in tabular form.
The blood tests that were performed were the anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA). In all positive tests two more specific CD blood tests were done as well.
The results in the table showed that the first degree relatives of CD patients are at a higher risk of developing he disease, even if they have no bowel symptoms (they may be incubating the disease before they even get CD). Second degree relative had about half the risk from first degree relatives. A surprisingly high number of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms do have CD (1 in 56 patients). The normal control group finding of 1 CD patient among 133 people was very similar to the European studies that had been published in the past.
| Celiac disease US study findings | |
| Patient group: |
Statistics: Frequency of CD in group |
| first degree relatives | 1 in 22 |
| second degree relatives | 1 in 39 |
| patients with gastrointestinal symptoms | 1 in 56 |
| normal control group | 1 in 133 |
Details about CD under this link: http://nethealthbook.com/digestive-system-and-gastrointestinal-disorders/celiac-disease/
Last edited October 25, 2014