It is a great challenge for persons who are suffering of drug addiction to quit. There is the difficult period of detoxification. Even though there is a lot of support, there will be intense withdrawal symptoms, and every drug free day is a hard won victory. It is a major milestone on the road to recovery to be discharged from a detox program, but the task to remain drug free and abstinent is anything but easy. For this reason it is of utmost importance that support to prevent a relapse is available in the form of counseling, support groups and a maintenance program which involves medication is accessible to the patient.
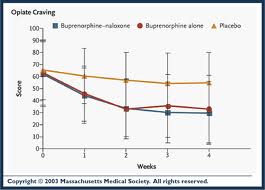
A standard treatment drug has been naltrexone which helped the recovering addict to remain abstinent. It has been largely used in patients who were recovering from heroin addiction. Dr. Richard Schottenfield from Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Ct. and colleagues led a randomized trial to compare the efficacy of the standard drug regimen of naltrexone with the medication Buprenorphine in patients who were in the process of receiving detoxification and drug counseling. A group of patients received placebo (sugar pills that contain no medication.) From the 126 detoxified heroin dependent patients 43 received the standard treatment of naltrexone, 44 received Buprenorphine and 39 took placebo pills.
The researchers found that patients who received Buprenorphine lasted nearly twice as long till they experienced a relapse than those who were on naltrexone and more than twice as long as compared to those who took placebo pills.HIV risk reduction behaviors were significantly reduced in all three groups. Maintenance treatment with Buprenorphine is a significant public health approach to reduce problems that are connected with heroin dependence and can make a difference to the recovering heroin addict on the path of abstinence from the drug.
More information about opium and heroin addiction: http://nethealthbook.com/drug-addiction/opium-heroin/
Reference: Lancet (2008) vol.371, pages 2192-2200 and 2150-2151
Last edited November 4, 2014