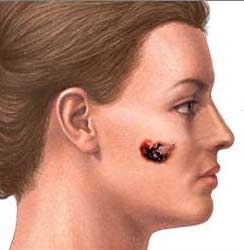
Scientists at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. have developed a modality of gene therapy to treat patients with melanoma.
The therapy alters the patients’ own lymphocytes to recognize and attack cancer cells. Dr. Steven Rosenberg and his team developed the new technique by drawing a blood sample containing normal lymphocytes from an advanced melanoma patient. Next the cells are infected with a retrovirus, which delivers genes that target specific receptors on T cells. Once the cells are infused back into the patient, these receptors attach themselves to the molecules on tumor cells and activate the lymphocytes to destroy the cancer cells. This method is called “adoptive cell transfer”. In early experiments there seemed to be little or no benefit, but researchers refined the methods and found valuable and promising aspects regarding the treatment of melanoma patients. It is crucial to administer the cells in their most active growth phase. This was shown in a group of 14 patients, where 2 terminal melanoma patients experienced cancer regression. Dr. Jeffrey Medin, head of the clinical research program in gene therapy at the Ontario Cancer Institute in Toronto agrees that this new therapy is a breakthrough as it has virtually brought terminal patients “back from the brink”. It is also exciting to see that the researchers could refine the techniques in order to create a more successful therapy. As a result the method will be more applicable to other cancers and broader populations.
Although adoptive cell transfer has only been used in melanoma patients so far, the researchers have shown ways to engineer cells of the immune system in a similar way to attack breast, liver cancer or lung cancers.
More information about treatment of melanoma: http://nethealthbook.com/cancer-overview/skin-cancer/melanoma/treatment-melanoma/
Reference: The Medical Post, September 19, 2006, page 1 and 61
Last edited November 1, 2014